Yerba mate tea is a South American herbal beverage that contains several beneficial components. I have already covered its health benefits and caffeine content in earlier articles.
In this article, we are going to dig deeper into yerba mate nutrition facts and the concentration of different bioactive compounds.
Here is a summary of Yerba Mate Nutrition Content:
- Calories: Yerba mate tea is relatively low in calories. It contains some carbohydrates and a very small amount of protein.
- Minerals: The most important minerals in yerba mate are iron and magnesium.
- Vitamins: Yerba mate has high vitamin B content, especially vitamins B1 (thiamin) and B6.
- Polyphenols: It has very high polyphenol content. These compounds act as antioxidants in our bodies and provide many health benefits.
- Xanthines: Contains three xanthines that are caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline. These molecules act as stimulants and provide a natural energy boost.
- Caffeoyl Derivatives: Yerba mate leaves contain several caffeoyl derivatives with antioxidant and neuroprotective effects.
- Saponins: Yerba mate is rich in saponins with anti-inflammatory properties.
See table 1 below for more detailed nutritional information of yerba mate brewed with 500 ml (17 oz) of water at 70 °C (158 °F) using 50 g (1.8 oz) of dry yerba mate. This is a typical amount of yerba mate consumed during one drinking session.
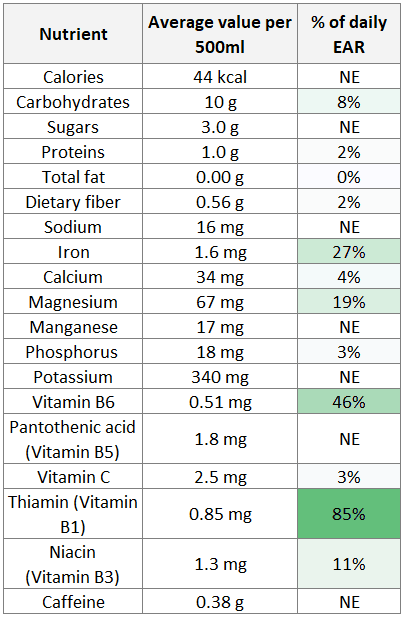
See the third column for the percentage of the EAR (Estimated Average Requirements) per day that the amount of each nutrient represents. The EAR value is the amount of nutrient that is expected to satisfy the needs of 50% of people for that particular nutrient. For some nutrients, the EAR is not established (NE).
Note that the amounts of nutrients can vary considerably depending on the yerba mate product and the brewing method used for preparing the infusion.
Polyphenols
Polyphenols are a group of phytochemicals that contain a benzene (C6H6) ring bound with a hydroxyl group(s) (-OH).
Many polyphenols act as antioxidants in our bodies and provide various health benefits.
Yerba mate contains 11 different types of polyphenols. The variety of yerba mate, how it has been processed, and the brewing method, all affect the concentration of polyphenols dissolved in yerba mate tea.
The types of polyphenolic compounds in mate tea differ significantly from the ones in green and black tea, mainly because yerba mate has a high concentration of chlorogenic acid but it doesn’t contain any catechins.
This means, that if you drink both yerba mate and green (or black) tea, they complement each other very well, and you can get a wide range of different beneficial polyphenols.
When compared to most other drinks, yerba mate tea has a much higher level of polyphenols.
Polyphenols are not the only antioxidants in mate tea but it seems their concentration has a strong correlation with the antioxidant capacity of a beverage.
See the chart below, where the total amount of polyphenols in different beverages is compared:
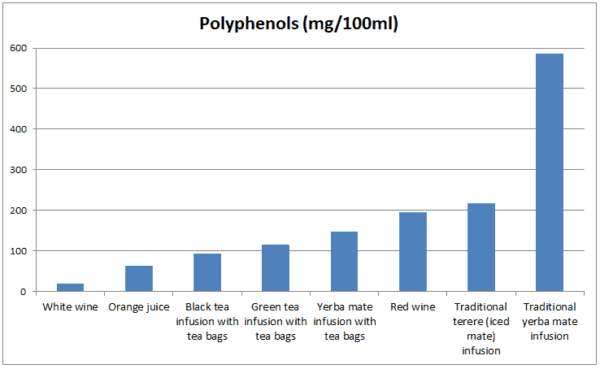
Note that yerba mate made with tea bags is not as strong as when it’s brewed with the traditional method, and thus, contains fewer polyphenols.
Xanthines
Xanthines are purine alkaloids with stimulant properties.
These compounds can be found in many different plants including yerba mate, coffee, tea, and chocolate.
Yerba mate tea contains three xanthines that are caffeine (1,3,7‐trimethylxanthine), theobromine (3,7‐dimethylxanthine), and theophylline (1,3‐dimethylxanthine).
In dry yerba mate leaves, the concentration of caffeine (1%-1.5%) is the highest of these three. Theobromine concentration is the second highest (0.3%-0.9%) while theophylline is present in a much smaller concentration.
The drying process of yerba mate leaves has a considerable effect on the concentration of caffeine and chlorophyll. When mate leaves are dried with a traditional method, including three different stages with different temperatures, the caffeine concentration decreases by 30% and the chlorophyll concentration by 70% to 80%.
However, when the tea is brewed with dry leaves it has more caffeine than if it is brewed with fresh leaves. This is likely to be explained by the disruption of cells and a decrease in moisture during the drying process.
Caffeoyl Derivatives
Yerba mate leaves contain several caffeoyl derivatives including caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid.
Caffeic acid has antioxidant capabilities that prevent oxidative stress, which helps with preventing DNA damage. Chlorogenic acid has a pivotal role in glucose and fat metabolism regulation.
In addition to polyphenols, caffeoyl derivatives can be considered as the major antioxidant compounds in yerba mate.
The chlorogenic acid and other compounds in yerba mate can also provide us with neuroprotective capabilities.
You can read more about yerba mate and brain in this article.
Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) belongs to the family of holly trees (Ilex), and while all of them contain caffeoyl derivatives, their concentration in yerba mate is significantly higher than in the other holly trees. The high concentration of these compounds is the main contributor to the high antioxidant capacity of yerba mate tea.
Saponins
Saponins are bitter-tasting compounds, with anti-inflammatory properties, and are found in many plants.
Yerba mate contains 19 different saponins, from which matesaponin D is the most abundant accounting for 30% of the total amount of saponins.
The saponins will form some foam on the surface when you brew yerba mate tea, as you can see in the image below:

Saponins stimulate the immune system and help your body with protection against pathogens.
In addition, many saponins found in yerba mate have antiparasitic properties. Saponins in yerba mate also have several other beneficial properties. They help with heart and artery function, protect the liver from damage, lower bad cholesterol, and increase metabolism.
Vitamins
Yerba mate tea contains a high amount of thiamin or vitamin B1.
Thiamin is essential for glucose metabolism and important for nerve, muscle, and heart functions. It is involved in the process of electrolytes flowing into and out of nerve and muscle cells. Just by drinking half a liter of yerba mate, you can already get about 85% of your daily need of thiamine.
Another vitamin found in abundance in yerba mate is vitamin B6.
Like thiamine, it plays an important role in our carbohydrate metabolism. In addition, it is important for fat metabolism and the creation of neurotransmitters and red blood cells. Yerba mate also contains pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), which is an essential nutrient necessary for making blood cells.
A relatively high amount of niacin (vitamin B3) is also present in yerba mate.
It acts as an antioxidant in our bodies and has an important role in the repairing of DNA and cell signaling function. It can also help with lowering cholesterol and boosting brain functions.
There is also some vitamin C in yerba mate tea, which, as we all know, is important for our health. However, the amount of vitamin C in mate tea is quite low, only a few milligrams in half a liter, while the estimated average requirement per day is 75 mg.
Minerals
Yerba mate tea is also a good source of minerals, mainly magnesium, potassium, manganese, and iron, which are important for human metabolism and development. Potassium might also assist with keeping blood pressure at lower levels, especially in people suffering from hypotension.
Final Thoughts on Yerba Mate Nutrition Facts
It is evident, that yerba mate contains an incredible amount of nutrients that are good for us.
I like to drink yerba mate tea mainly because of its energizing effect and great taste. But the fact that it also provides us with so many beneficial and nourishing substances, is also very important to me.
There are several great yerba mate products to choose from. Check out the reviews here to find the right one for you!
I hope this article provided you with sufficient information related to yerba mate nutrition content. If you have any questions or comments related to yerba mate nutrition facts, you can post them below.
Enjoy your nutritious Yerba Mate Tea!
-Joonas







This is so awesome! I actually am in the market for a multivitamin or supplement and Yerba seems to be packed with the exact things I’ve been looking for! I am definitely going look into purchasing some and giving this a try.
Hello Katie,
Yes, you should definitely try it! There are also yerba mate extracts available. I will be writing an article about them soon, so stay tuned.
-Joonas
This is a great post and I agree with Katie,
about using yerba mate as a supplementation
to my diet.
But what would have been great if I could just
click somewhere after the post to purchase it.
I will purchase it so why not be from you?
Just saying.
Hi Cindy!
Nice to hear that you liked my article.
You can read this review article to find a good yerba mate to buy: https://yerbamateculture.com/yerba-mate-tea-reviews-5-popular/
Just click on the product picture to order it from Amazon.
You can also check out the other review articles here on my site.
-Joonas
Hi there! First and foremost I just want to say that your explanations were very detailed and well explained. Thanks for making things clearer for me I really appreciate it.
Well wishes,
Azfar
Hi Azfar!
Good to hear that you found my article useful.
All the best,
Joonas
Hi. Did you make a mistake on the amount of a 17 oz drink?? I use a tablespoon per 8 oz’s.
Hi Leonardo,
Do you mean if there is a mistake here “yerba mate brewed with 500 ml (17 oz) of water at 70 °C (158 °F) using 50 g (1.8 oz) of dry yerba mate”? That maybe 50g (1.8 oz) is too much dry yerba mate for that amount of water?
I believe there is no mistake. If you brew yerba mate with the traditional method (gourd and bombilla) you really use a lot of mate. Then you actually add more water up to 20 times, so you can make several brews from the same mate.
Also, if you look at the chart about polyphenols, you can notice that when you make yerba mate with tea bags the polyphenol content is much lower than with traditional method. This applies to other nutrients as well because the infusion is milder.
If you want to know more about brewing yerba mate tea, I recommend checking out this article: https://yerbamateculture.com/how-to-brew-yerba-mate-tea/
See also this study where they mention using 50 g (1.8 oz) of dry mate for 500 ml of water: https://www.bombisha.com.au/yerba-mate/yerba-mate-antioxidant-study/